Platform-Independent
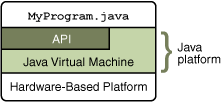
A platform is the hardware or software environment in which a program runs. Some of the most popular platforms are Microsoft Windows, Linux, Solaris OS, and Mac OS. Most platforms can be described as a combination of the operating system and underlying hardware. The Java platform differs from most other platforms in that it’s a software-only platform that runs on top of other hardware-based platforms.
The Java platform has two components:
-
The Java Application Programming Interface (API)
The API is a large collection of ready-made software components that provide many useful capabilities. It is grouped into libraries of related classes and interfaces; these libraries are known as packages. - The Java Virtual Machine
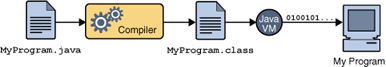
In the Java programming language, all source code is first written in plain text files ending with the .java extension. Those source files are then compiled into .class files by the javac compiler. A .class file does not contain code that is native to your processor; it instead contains bytecodes — the machine language of the Java Virtual Machine (Java VM). The java launcher tool then runs your application with an instance of the Java Virtual Machine.
Because the Java VM is available on many different operating systems, the same .class files are capable of running on Microsoft Windows, the Solaris Operating System (Solaris OS), Linux, or Mac OS. (Write Once Run Everywhere)
References :